| ○
|
||
| 2010 | ||
| ○
|
||
|
|
||
| ○
|
||
| 2007 | ||
 |
|
|
| October 2006 | ||
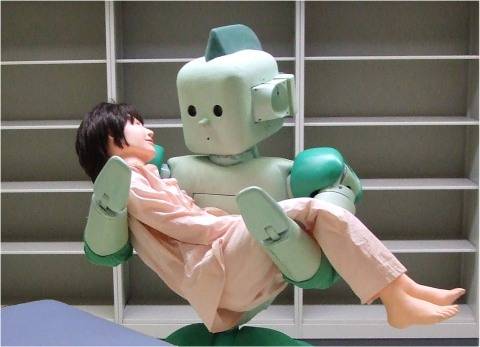 |
Ri man
|
|
| 2006 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2006 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2006 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2006 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2005 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2005 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2005 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2005 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2005 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2004 | ||
| ○
|
||
| 2004 | ||
 |
Snuggling Ifbot
|
|
| 2004 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2004 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2004 | ||
 |
QRIO conducted the Tokyo Philharmonic Orchestra
|
|
| 2004 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| January 25, 2004 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| January 2004 | ||
 |
|
|
| January 4, 2004 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2003 | ||
 |
Tmsuk's Banryu
|
|
| 2003 | ||
 |
ApriAlpha
|
|
| 2003 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2003 | ||
| ○
|
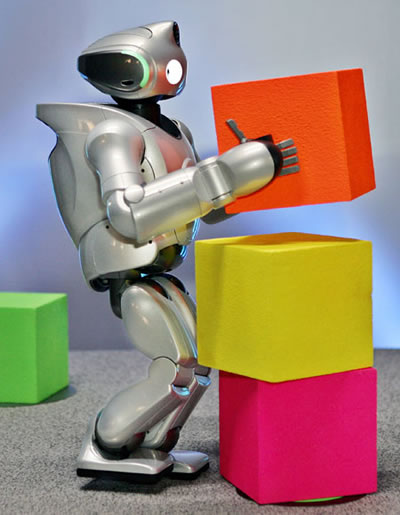
Sony's SDR-4X
|
|
| 2002 | ||
 |
Fujitsu's Maron-1
|
|
| 2002 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2002 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2001 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2001 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2001 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2001 | ||
| ○
|
Robodex
|
|
| 2000 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2000 | ||
 |
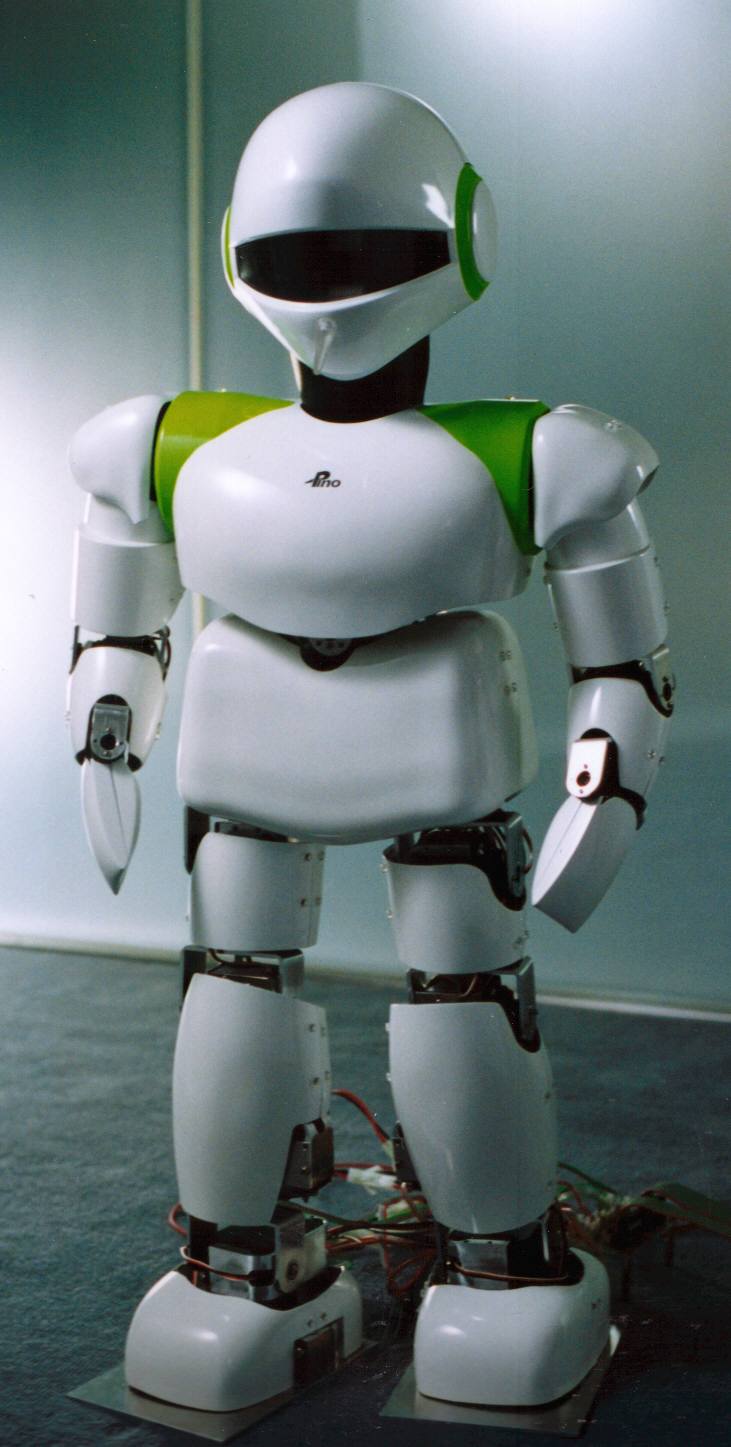
ASIMO is a humanoid robot
|
|
| 2000 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| 1999 | ||
| ○
|
Extreme machines: Incredible robots
|
|
| 1999 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1999 | ||
| ○
|
Personal Robots released the Cye robot it performed a vairety of household chores, such as deliver mail, carry dishes, and vacuum. It was created by Probotics Inc.
|
|
| 1999 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1998 | ||
 |
|
|
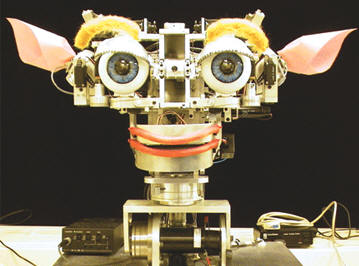
| 1998 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1998 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1997 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1997 | ||
 |
|
|
| July 4, 1997 | ||
 |
Deep Blue became the first computer system to defeat a reigning world champion in a match under standard chess tournament time controls
|
|
| May 11, 1997 | ||
 |
|
|
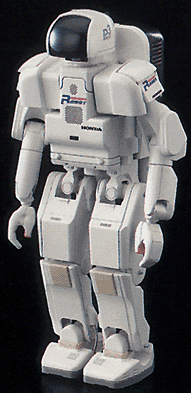
| 1997 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| 1997 | ||
| ○
|
RoboTuna was created by David Barrett at MIT
|
|
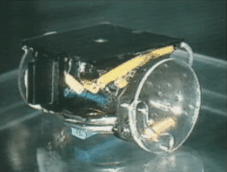
| 1996 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1996 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1995 | ||
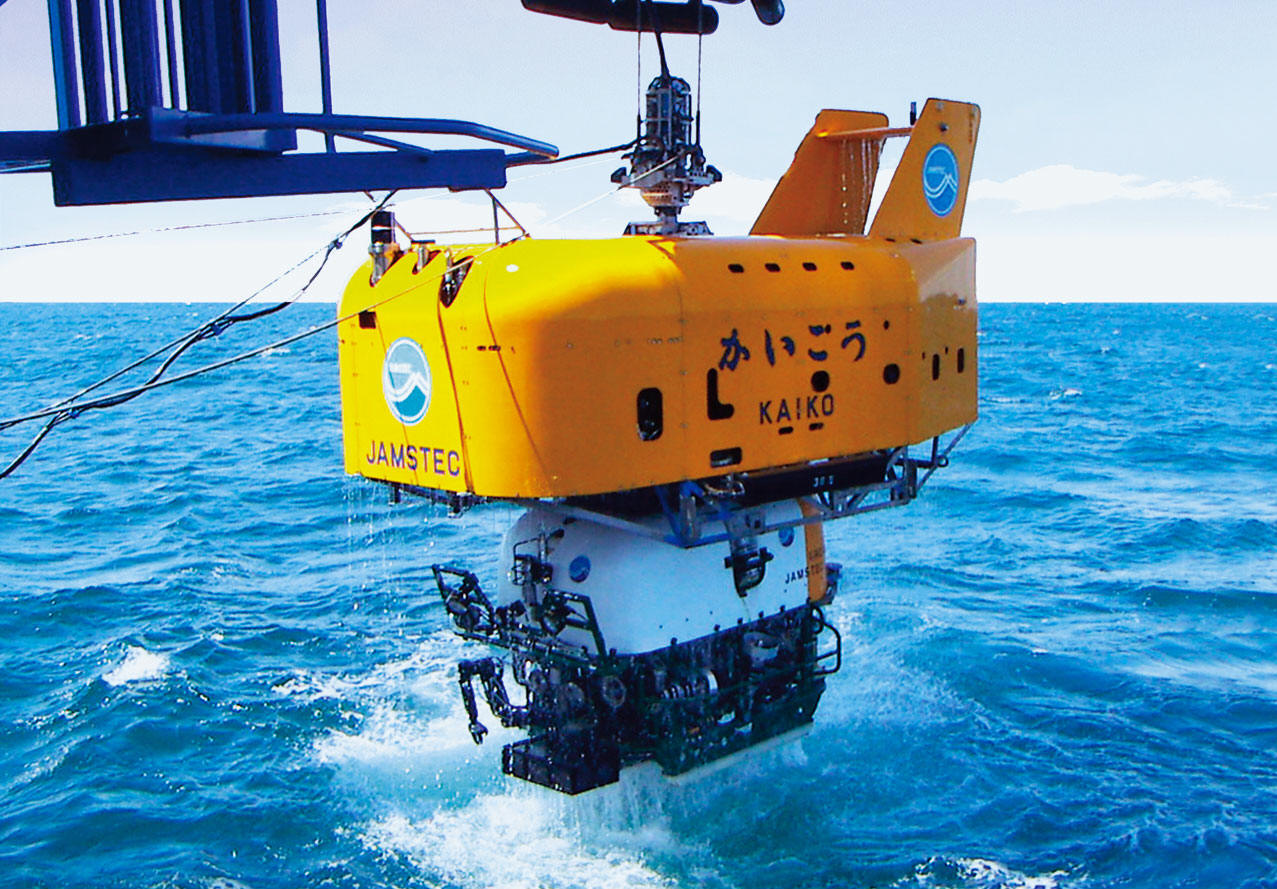 |
|
|
| 1995 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1994-2002 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
| ○
|
|
|
 |
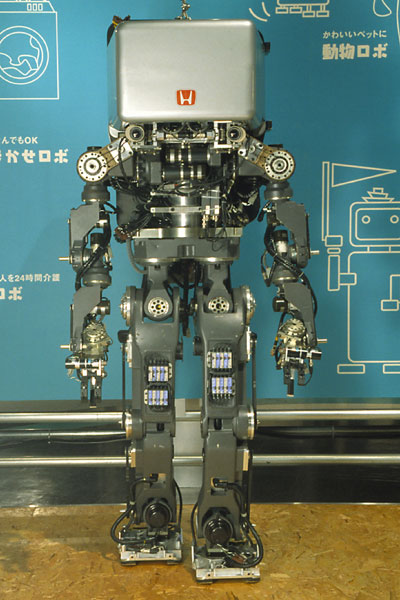
Seiko's Monsieur
|
|
| 1993 | ||
 |
|
|
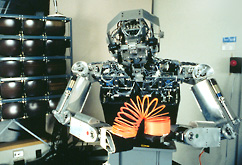
| 1993 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1993 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| early 1990s | ||
| ○
|
the NASA Space Telerobotics Program
|
|
| 1992-1997 | ||
 |
Ambler
|
|
| 1990 | ||
| ○
|
Robodoc performed a hip-replacement operation on a dog (1992 on a human patient)
|
|
| 1990 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1988 | ||
| ○
|
the first HelpMate robot went to work at Danbury Hospital in Conneticut
|
|
| 1988 | ||
| ○
|
K. Eric Drexler's Engines of Creation
|
|
| 1986 | ||
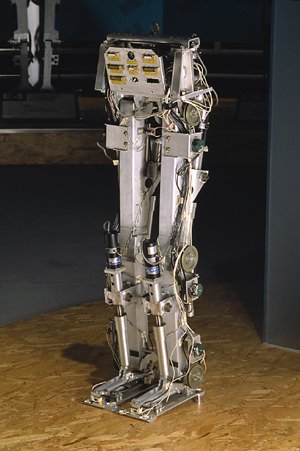 |
|
|
| 1986 | ||
| ○
|
the NASA Automation and Robotics Program
|
|
| 1985 | ||
| ○
|
created by the General Robotics Corp. the RB5X was a programmable robo it had infrared sensors, romote audio/video transmission, bump sensors, and a voice synthesizer. It had software that could enable it to learn about its environment
|
|
| 1985 | ||
 |
the Omnibot 2000, a toy robot was created by the Tomy Kyogo Company Inc. It was controlled by a hand-held remote control or through programs stored on magnetic tape
|
|
| 1985 | ||
 |
Ichiro Kato created WABOT II that read music and plays an electronic organ
|
|
| 1984 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1984 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1984 | ||
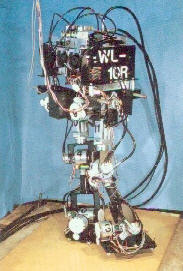 |
Ichiro Kata built the WL-10R it had more degrees of freedom then its predessor. It could walk laterally, turning and walking forward as well as backward. It could take a step every 4.4 seconds
|
|
| 1983 | ||
| ○
|
the Heathkit Corporation designed Hero Jr. it was intented to be a home companion. It had an alarm clock, and it could sing several songs. Additional programs were stored on 250 cartridges
|
|
| 1982 | ||
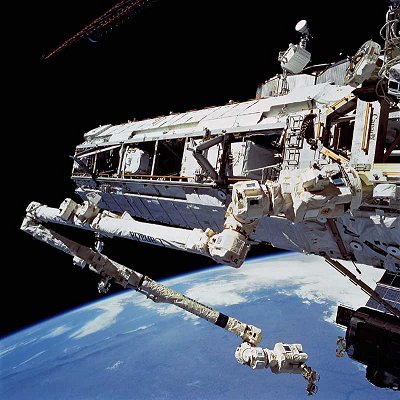 |
|
|
| 1981 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1979 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1978 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1978 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1977 | ||
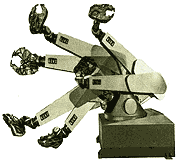 |
|
|
| 1973 | ||
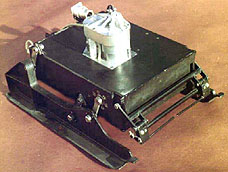 |
|
|
| 1971 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1970 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1970 | ||
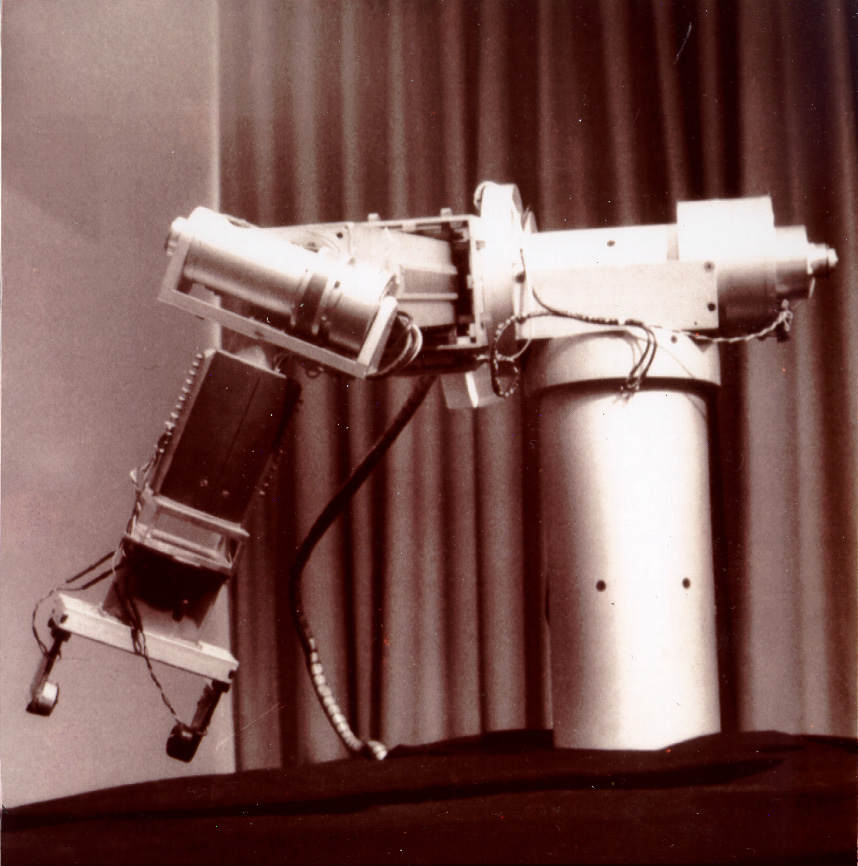 |
|
|
| 1969 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1968 | ||
 |
|
|
| April 20, 1967 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| 1966 | ||
| ○
|
the first expert system, DENDRAL was created by a team at Stanford. The team was lead by Ed Feigenbaum. The robot was designed to execute the accumulated knowledge of experts
|
|
| 1965 | ||
 |
the Rancho-Arm
|
|
| 1963 | ||
| ○
|
General Motors installed the first industrial robot, the Unimate, on a production line
|
|
| 1962 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1961 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1960 | ||
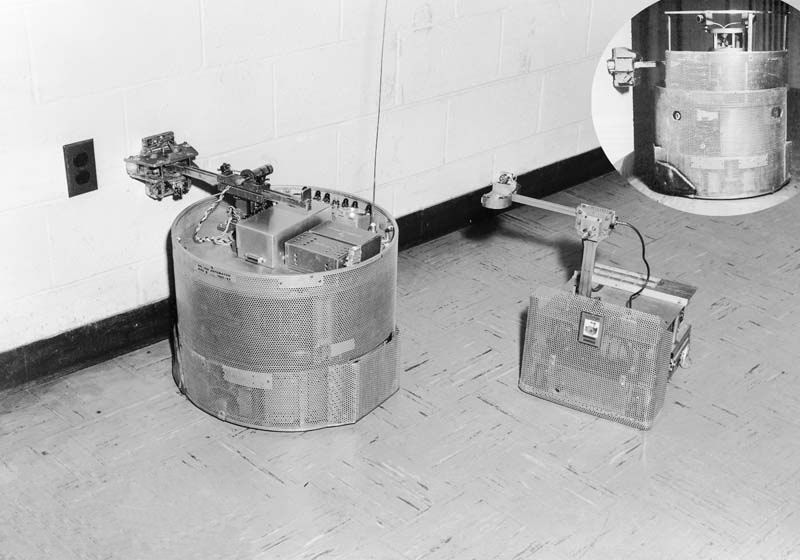 |
Hopkins Beast
|
|
| 1960 | ||
| ○
|
John McCarthy and Marvin Minsky founded the Artificial Intelligence Laboratory at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
|
|
| 1958 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| ○
|
the Dartmouth Summer Research Conference on Artificial Intelligence
|
|
| 1956 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1954 | ||
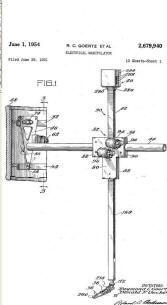 |
a teleoperator-equipped articulated arm was designed by Raymond Goertz for the Atomic Energy Commission
|
|
| 1951 | ||
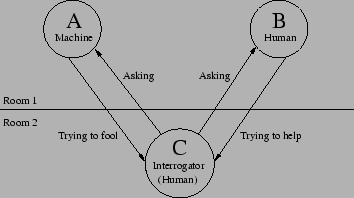 |
|
|
| 1950 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1950 | ||
 |
the Transistor was invented at Bell Telephone Laboratories by John Bardeen, Walter Houser Brattain, and William Bradford Shockley
|
|
| December 1947 | ||
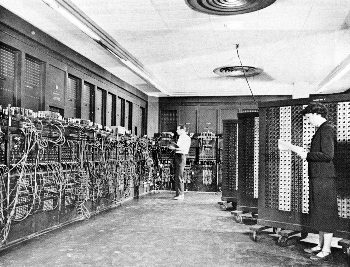 |
the ENIAC short for Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer, was the first all-electronic computer designed to be Turing-complete
|
|
| February 1946 | ||
| ○
|
George Devol patented a general purpose playback device for controlling machines using magnetic recordings
|
|
| 1946 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1944 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
| ○
|
the word robotics was first used in print by Isaac Asimov, in his science fiction short story Runaround
|
|
| 1941 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1940s | ||
 |
|
|
| 1940 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1940 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1936 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1927 | ||
 |
Rossum's Universal Robots is a science fiction play by Karel Čapek which introduced and popularized the term robot
|
|
| 1921 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1917 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| early 20th century | ||
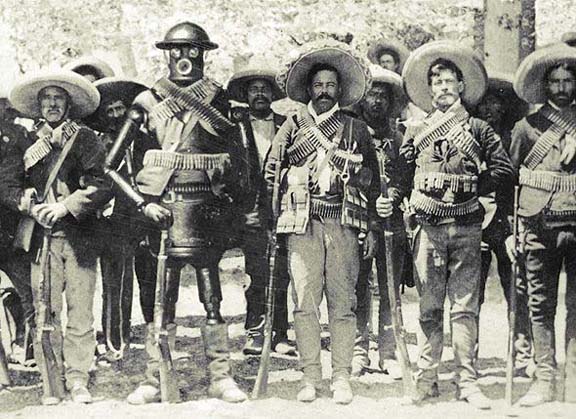 |
|
|
| 1893 | ||
| ○
|
Frank Reade Jr. built the Electric Man which is more-or-less an electric version of the Steam Man
|
|
| 1885 | ||
| ○
|
John Brainerd creates the Steam Man apparently used to pull things
|
|
| 1865 | ||
 |
Mary Shelley's Frankenstein
|
|
| 1818 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| 1801 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1770 | ||
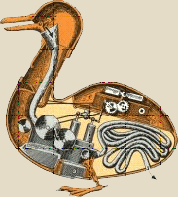 |
Jacques de Vaucanson's Digesting Duck
|
|
| 1739 | ||
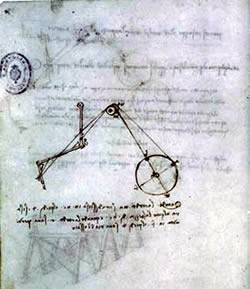 |
|
|
| 1495 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1305 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1205 | ||
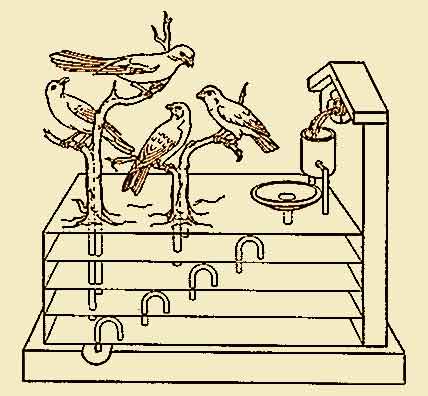 |
the automata of Ancient Greece
|
|
 |
in Greek mythology, Hephaestus (the god of metal work) created mechanical servants, including intelligent female slaves and automated furniture
|
|