| ○
|
|
|
| ○
|
|
|
| August 19, 2010 | ||
| ○
|
HP bought Palm for around $1.2 bn US
|
|
| April 28, 2010 | ||
|
|
|
|
| January 27, 2010 | ||
|
|
|
|
| 2010 | ||
|
|
|
|
| October 22, 2009 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2008 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2008 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2007 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2007 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2007 | ||
 |
|
|
| January 30, 2007 | ||
| ○
|
AMD merged with ATI
|
|
| October 25, 2006 | ||
 |
|
|
| July 2006 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| April 25, 2006 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2006 | ||
| ○
|
Adobe Systems bought Macromedia
|
|
| December 3, 2005 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2005 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2005 | ||
|
|
|
|
| October 25, 2005) | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2005 | ||
| ○
|
One billion people have access to the internet
|
|
| 2005 | ||
| ○
|
the Pentium D contains two Pentium 4 Prescott dies, unlike other multicore processors which place both cores on a single die
|
|
| 2005 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2005 | ||
 |
|
|
| February 2005 | ||
 |
the Columbia is currently the second fastest computer in the world running at 51.9 teraflops, or 51.9 trillion floating point calculations per second. It knocked NEC's Earth Simulator off its perch as the world's No. 1 machine - a spot it had held since 2002, before it was surpassed in turn by the Blue Gene/L
|
|
| October 2004 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2004 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2004 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2004 | ||
|
|
|
|
| 2004 | ||
| ○
|
Microsoft was granted a patent on the double-click by the US Patents and Trademark Office
|
|
| April 27, 2004 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| April 2004 | ||
 |
smartphones began to make up an increasingly large part of the mobile phone market
|
|
| 2004 | ||
 |
the Blue Gene/L is currently the fastest computer with a theoretical peak performance of 360 TFLOPS. On June 22, 2006, NNSA and IBM announced that Blue Gene/L has achieved 207.3 TFLOPS
|
|
| 2004 | ||

|
|
|
| 2004 | ||
| ○
|
SWsoft acquired the control panel companies Plesk and Confixx
|
|
| 2003 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| July 2003 | ||
 |
64 bit processors started being offered for home use with the Apple Power Mac G5, the Athlon 64, and the Itanium, which had been introduced by Intel already in 2001
|
|
| June 23, 2003 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2003 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2003 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 200? | ||
 |
|
|
| 2003 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| March 2003 | ||
 |
|
|
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
| ○
|
Digital terrestrial television
|
|
| 2002 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2002 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2002 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2002 | ||

|
|
|
| 2002 | ||
 |
|
|
| October 25, 2001 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 2001 | ||
 |
Wikipedia began as a complement to the expert-written Nupedia. It is edited by volunteers in wiki fashion, meaning articles are subject to change by nearly anyone
|
|
| January 15, 2001 | ||
|
the Google search engine rose to prominence. Its success was based in part on the concept of link popularity and PageRank. Google, Inc. was established in 1998
|
|
| 2001 | ||
| ○
|
300,000,000 computers on the Internet
|
|
| 2001 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| November 2000 | ||
|
Opera introduced tabbed browsing
|
|
| 2000 | ||
| ○
|
Plesk released the first version of its hosting control panel
|
|
| 2000 | ||
 |
ASIMO is a humanoid robot
|
|
| 2000 | ||
|
rss is a family of xml formats
|
|
| 2000 | ||
 |
|
|
 |
flat panel displays started to replace cathode ray tube desktop monitors. Liquid crystal displays were already invented in 1971 by James Fergason
|
|
| 2000 | ||
 |
Judge Jackson ordered that Microsoft split into two companies during the antitrust trial in which the U.S. Department of Justice, joined by twenty U.S. states, alleged that Microsoft abused monopoly power. A year later the Bush administration Justice Department announced that it will no longer seek a breakup of Microsoft (Sept. 6, 2001). Already on January 13, 2000 Bill Gates had created a new role for himself -- chairman and chief software architect. Steve Ballmer became president and CEO
|
|
| June 7, 2000 |
|
|
 |
the AMD Athlon was the first chip to reach the 1 GHz mark. Intel came out with the 1GHz Intel Pentium III processor on March 8, 2000
|
|
| 2000 | ||
 |
|
|
| 2000 | ||
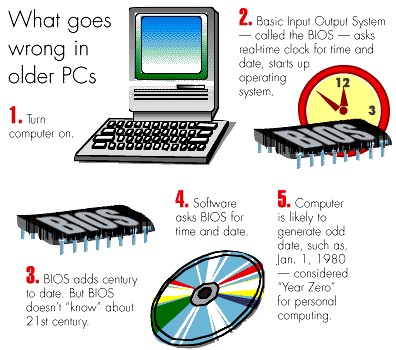 |
the Y2K bug turned out not to have occurred on most computers
|
|
| 1999-2000 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1999 | ||
 |
Bluetooth is an industrial specification for wireless personal area networks
|
|
| May 20, 1999 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| April 1999 |
|
|
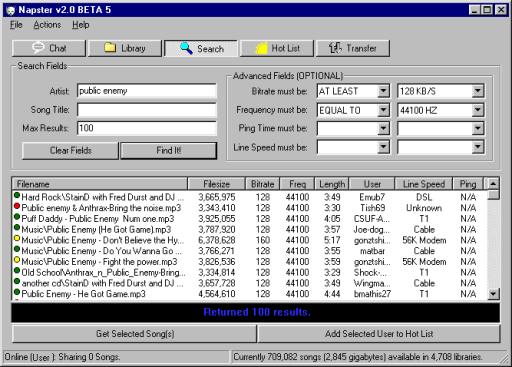 |
Napster was the first peer-to-peer file sharing network. It was developed by Shawn Fanning
|
|
| 1999 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1999 | ||

|
ADSL was introduced in many countries with downstream rates starting at 256 kbit/s and 8 Mbit/s as the current maximum transfer speed
|
|
| 1999 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| December 1998 |
|
|
 |
ICANN is the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers
|
|
| September 18, 1998 | ||
 |
|
|
|
|
||
 |
the Eiger Labs MPMan F10 was the first digital audio player on the American market
|
|
| 1998 | ||
 |
the rocket e book
|
|
| 1998 | ||
| ○
|
Intel released the Accelerated Graphics Port specification
|
|
| 1997 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1997 | ||
 |
|
|
| 90s | ||
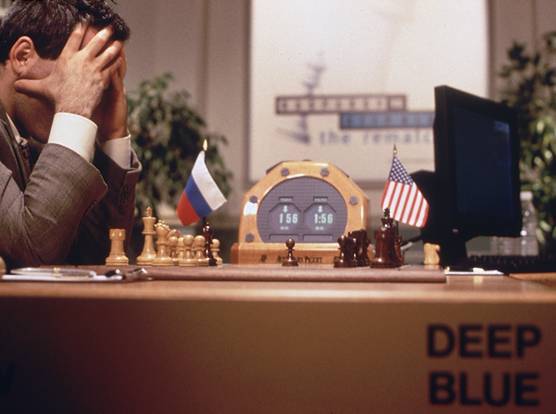 |
IBM's supercomputer Deep Blue beat chess master Garry Kasparov in a six-game match, in a dramatic reversal of their battle the previous year
|
|
| May 1997 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1997 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| late 1990s | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1996 | ||
|
|
|
|
| 1996 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1996 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| November 1996 | ||
 |
the Tamagotchi is a handheld virtual pet
|
|
| November 1996 | ||
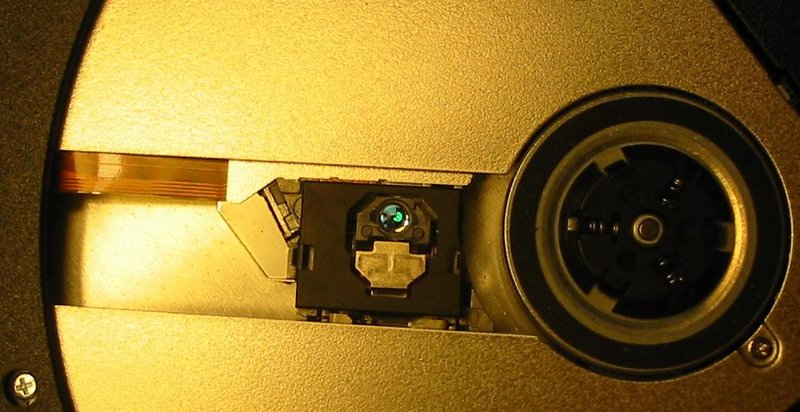 |
the first DVD players and discs became available in Japan and in March of 1997 in the United States. By the spring of 1999, the price of a DVD player had dropped below the US $300 mark. At that point Wal-Mart began to offer DVD players for sale in its stores
|
|
| November 1996 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| July 4, 1996 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| July 1, 1996 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1996 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1996 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1996 | ||

|
the Apache HTTP Server became the most popular server on the net
|
|
| April 1996 | ||
 |
the Palm Pilot PDA was released
|
|
| 1996 | ||
| ○
|
21,000,000 computers on the Internet the number of computers online had exceeded 10 000 in 1987, 100 000 in 1989, and 1 million in 1992. Also in 1992 the term "surfing the net" was coined by Jean Armour Polly |
|
| 1996 | ||
|
|
Java 1.0 was released after five years of development by James Gosling and colleagues
|
|
| 1996 | ||
| ○
|
MultiTorg Opera
|
|
| 1995 | ||
 |
Dragon released discrete word dictation-level speech recognition software. It was the first time dictation speech recognition technology was available to consumers. IBM and Kurzweil followed a few months later. In 1997 Dragon introduced "Naturally Speaking", the first "continuous speech" dictation software available (meaning you no longer need to pause between words for the computer to understand what you're saying)
|
|
| 1995 | ||
 |
FrontPage was initially created by the Cambridge, Massachusetts company Vermeer Technologies Incorporated. Vermeer was acquired by Microsoft in 1996
|
|
| 1995 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1995 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1995 | ||
 |
VeriSign is a company that operates a diverse array of network infrastructure, including two of the Internet's thirteen root nameservers
|
|
| 1995 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| November 1995 | ||
 |
eBay hosted its first auction
|
|
| September 4, 1995 | ||
 |
|
|
| August 24, 1995 | ||
| ○
|
the NSFNET Backbone Service, operating since 1987, was successfully transitioned to a new architecture, where traffic is exchanged at interconnection points called Network access points
|
|
| April 30, 1995 | ||

|
PHP is one of the most popular server-side scripting systems on the net
|
|
| June 8, 1995 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| March 1995 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1994 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1994 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1994 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 19?? | ||
| ○
|
America Online announced that it had reached 1 million subscribers
|
|
| 1994 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1994 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1994 |
|
|
 |
Justin Hall who began eleven years of personal blogging while a student at Swarthmore College, is generally recognized as one of the earliest bloggers. The term "weblog" was coined by Jorn Barger in December 1997. The shorter version, "blog", was coined by Peter Merholz, who, in April or May of 1999, broke the word weblog into the phrase "we blog" in the sidebar of his weblog. This was interpreted as a short form of the noun and also as a verb to blog, meaning "to edit one's weblog or a post to one's weblog". Usage spread during 1999, with the word being further popularized by the near-simultaneous arrival of the first hosted weblog tools: Evan Williams and Meg Hourihan's company Pyra Labs launched Blogger (which was purchased by Google in February 2003) and Paul Kedrosky's GrokSoup. As of March 2003, the Oxford English Dictionary included the terms weblog, weblogging and weblogger in their dictionary
|
|
| 1994 | ||

|
Amazon.com was one of the first major companies to sell goods over the Internet
|
|
| 1994 | ||
|
the World Wide Web Consortium creates standards that Web developers should try to conform to, in order to maximize the ability of others to access their Web sites
|
|
| 1994 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1993 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1993 | ||
 |
sub-notebooks at the time of its introduction, the HP Omnibook 300 was the smallest and lightest PC on the market to feature a full-size keyboard and full VGA
|
|
| 1993 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1993 | ||
| ○
|
the first Def Con hacking conference took place in Las Vegas
|
|
| July 9, 1993 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| July 1993 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| July 1993 | ||
|
the World Wide Web Wanderer was a perl based web crawler that was first deployed to measure the size of the World Wide Web. The Software was developed at MIT by Matthew Gray. Later in 1993, it was used to generate an index called the "Wandex", providing the first search engine on the web
|
|
| June, 1993 | ||
 |
Peripheral Component Interconnect
|
|
| 1993 | ||
 |
the Mosaic web browser written at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications, has been described as "the killer application of the 1990s" because it was the first program to provide a slickmultimedia graphical user interface to the Internet's burgeoning wealth of distributed information services (formerly mostly limited to FTP, Usenet and Gopher) at a time when access to the Internet was expanding rapidly outside its previous domain of academia and large industrial research institutions. The company producing the software was founded as Mosaic Communications Corporation on April 4, 1994 by Marc Andreessen and Jim Clark, and was the first company to attempt to capitalize on the nascent World Wide Web. It released a web browser called Mosaic Netscape 0.9 on October 13, 1994. This browser was subsequently renamed Netscape Navigator, and the company took on the 'Netscape' name on November 14, 1994. In January 1998 Netscape open sourced its Web browser as the Mozilla Project. On November 24, 1998 America Online announced it would acquire Netscape Communications in a tax-free stock-swap valued at US$4.2 billion at the time of the announcement |
|
| April 22, 1993 | ||
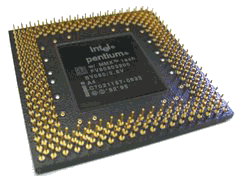 |
the earliest Pentiums were released at the clock speeds of 66 MHz and 60 MHz. Later on 75, 90, 100, 120, 133, 150, 166, 200 and 233 MHz versions gradually became available. Other versions of the Pentium line include the Pentium Pro (November 1995), the Pentium II (May 7, 1997), the Pentium III (March 2000) and the Pentium 4 which was released in November 2000
|
|
| March 22, 1993 | ||
 |
|
|
| March 1993 | ||
 |
the Internet Society is the parent corporation of the Internet Architecture Board and the Internet Engineering Task Force
|
|
| 1992 | ||
 |
Windows 3.1 was released two years after Version 3.0
|
|
| August 1992 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1992 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1992 | ||
 |
SAP R/3 is one of the most popular ERP (Enterprise resource planning systems) software products. These are management information systems that integrate and automate many of the business practices associated with the operations or production aspects of a company
|
|
| July 6, 1992 | ||
 |
the SupraFax 14400 ran at the 14.4 kbit/s rate
|
|
| 1991 | ||
| ○
|
the Advanced Computing Environment
|
|
| 1991 |
|
|
| ○
|
|
|
| 1991 |
|
|
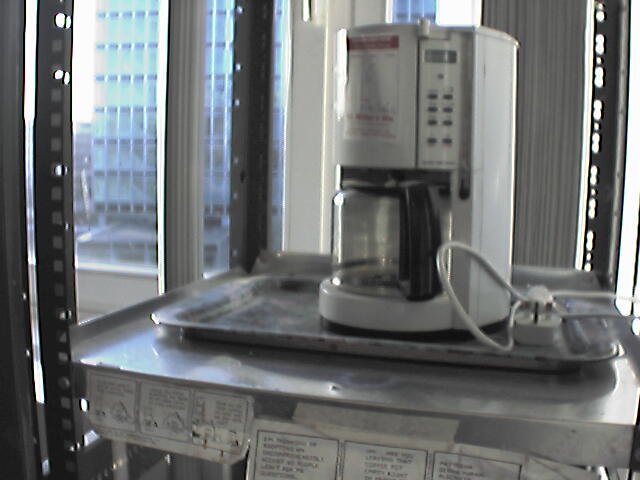 |
the Trojan room coffee pot was the inspiration for the world's first webcam
|
|
| 1991 | ||
 |
Linux is a computer operating system which is written by many programmers at once in a process called open-source development. The software was originally programmed by Linus Torvald only, with the aim to develop a capable UNIX operating system that could be run on a PC. It was inspired by Minix (a kernel and operating system developed by Andrew Tanenbaum)
|
|
| September 1991 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1991 | ||
 |
|
|
| August 6, 1991 | ||
 |
Visual Basic 1.0 was released for Windows
|
|
| May 1991 | ||
 |
second generation mobile phone systems such as GSM, IS-136 ("TDMA"), iDEN and IS-95 ("CDMA") began to be introduced. The first digital cellular phone call was made in the United States in 1990, in 1991 the first GSM network opened in Europe
|
|
| 1991 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1990 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1990 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1990 | ||
| ○
|
the Electronic Frontier Foundation was formed by Mitch Kapor and John Perry Barlow in part to defend the rights of those investigated for alleged computer hacking
|
|
| 1990 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1990-1993 |
|
|
| ○
|
|
|
| May 22, 1990 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
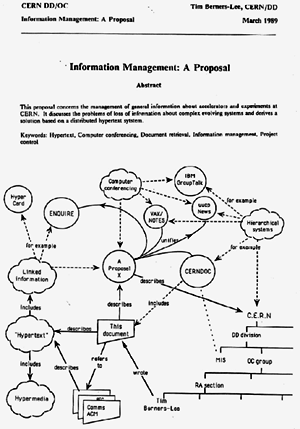 |
the www as well as http, html and urls were invented by Tim Berners-Lee at Cern
|
|
| 1990 | ||
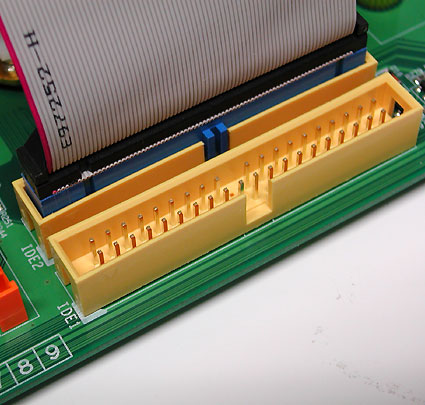 |
Advanced Technology Attachment
|
|
| 1989 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1989 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1989 | ||
| ○
|
Silicon Graphics introduced what was arguably the first 3D graphics workstation the IRIS 4D Superworkstation
|
|
| 1989 | ||
| ○
|
the first dial-up internet service provider was world.std.com
|
|
| 1989 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1989 | ||
 |
|
|
| April 21, 1989 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1989 | ||
 |
the GNU General Public License is the most popular license for free software
|
|
| January 1989 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1988 | ||
| ○
|
the Moving Picture Experts Group
|
|
| 1988 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1988 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| August 1988 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1988 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1988 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1988 | ||
 |
most dialup modems follow the Hayes Command Set it was originally developed for the Hayes Smartmodem 2400
|
|
| 1988 | ||
 |
|
|
| late 80s | ||
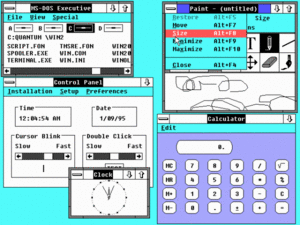 |
Windows 2.0 was released, with icons & overlapping windows
|
|
| December 9, 1987 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1987 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1987 | ||
 |
the mp3 format for digital audio encoding was invented by Karlheinz Brandenburg and Jürgen Herre of the "Fraunhofer Institute for Integrated Circuits." In the first half of 1995, mp3 files began flourishing on the Internet
|
|
| 1987 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1987 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1987 | ||
 |
the first digital desktop slide scanner was produced by Barneyscan
|
|
| 1987 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1987 | ||
| ○
|
Congress passed the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act
|
|
| 1986 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1986 | ||
 |
386 CPU's were the standard for IBM PCs until the introduction of the 486 CPU in April 1989. The predecessor of the 80386 was the Intel 80286, a 16-bit processor with a segment-based memory management and protection system. The 80386 added a 32-bit architecture and a paging translation unit, which made it much easier to implement operating systems which used virtual memory. The first 80386-based PC was the Compaq Deskpro 386 introduced in September 1986
|
|
| 1986 | ||
 |
the IBM Convertible was the first real laptop
|
|
| April 1986 | ||
| ○
|
Loyd Blankenship's Hacker Manifesto
|
|
| 1986 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1985 | ||
| ○
|
the Hacker zine Phrack was first published by Craig Neidorf ('Knight Lightning') and Randy Tischler
|
|
| 1985 | ||
| ○
|
Aldus PageMaker was the first desktop publishing program
|
|
| 1985 | ||
| ○
|
NeXT was founded by Steve Jobs after his resignation from Apple Computer. Apple Computer acquired NeXT in 1997 in order to use the OpenStep operating system as the basis for Mac OS X
|
|
| 1985 | ||
 |
Microsoft Windows 1.0 was Microsoft's first attempt to implement a multitasking graphical user interface-based operating environment on the PC platform. The program has by now come to dominate the world market for personal computer with a market share estimated to be around 95% for desktop personal computers. Developement on the project named "Interface Manager" started in September 1981
|
|
| November 1985 | ||
 |
the File Transfer Protocol was first developed in 1971 for implementation on hosts at M.I.T. In 1985 ftp was defined by the RFC 959 documnet
|
|
| October 1985 | ||
 |
the CD-ROM was introduced
|
|
| 1985 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| mid-1980s | ||
| ○
|
Out of the Inner Circle: A Hacker's Guide to Computer Security by Bill Landreth and Howard Rheingold
|
|
| 1985 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1985 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1980s | ||
| ○
|
|
|
 |
the Amiga 1000 was followed up with the introduction of the A500 and A2000 models in 1987 and the A3000 in 1990
|
|
| 1985 | ||
| ○
|
Cisco Systems created the first commercially successful multi-protocol router
|
|
| 1984 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1984 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1984 | ||
| ○
|
2600: The Hacker Quarterly was founded by Eric Corley
|
|
| 1984 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1984 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1984 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| June 1984 | ||
 |
FidoNet was started by Tom Jennings of San Francisco, California as a means to network together BBSes or mailboxes (like MausNet) that used his own "Fido" BBS software
|
|
| 1984 | ||
 |
|
|
| January 1984 | ||
|
Symbolics.com
|
the Domain Name System was introduced by Paul Mockapetris. Symbolics.com became the first registered commercial domain name |
|
| 1984 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| December 1983 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1983 | ||
 |
VisiOn was the first integrated graphical software environment for IBM PCs
|
|
| December 1983 | ||

|
Microsoft Word took many concepts and ideas from Bravo, the original GUI word processor developed at Xerox PARC by Charles Simonyi. Later versions were created for the Apple Macintosh (1984), SCO UNIX, and Microsoft Windows (1989)
|
|
| November 1983 | ||
 |
the Nintendo Famicom was released in its American and European version as the NES video game console in June 1985
|
|
| July 1983 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1983 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1983 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1983 | ||
 |
the biggest-selling early laptop was the Kyocera Kyotronic 85
|
|
| 1983 | ||
| ○
|
the HP-150 was one of the world's earliest commercialized touch screen computers
|
|
| 1983 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1983 | ||
 |
Lotus 1-2-3 is a spreadsheet program which was the IBM PC's first killer application
|
|
| January 26, 1983 | ||
 |
the Apple Lisa was the second computer with a graphical user interface (GUI) after the Xerox Alto. Nevertheless it became a commercial failure due to its price of $9,995
|
|
| January 1983 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1983 | ||
 |
the TCP/IP protocol began to be used for ARPAnet and the Defense Data Network
|
|
| January 1, 1983 | ||
 |
the Commodore 64 with estimated sales between 17 and 25 million units became and remains the best-selling computer model of all time
|
|
| August 1982-1993 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1982 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1982-1986 | ||
 |
the 3 1/2-inch hard cartridge disk standard
|
|
| 1982 | ||
 |
|
|
| July 1982 | ||
 |
the GRiD Compass 1100 was arguably the first laptop computer
|
|
| April 1982 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1982 | ||
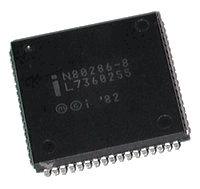 |
the Intel 80286 was initially released in 6 and 8 MHz editions, and subsequently scaled up to 20 MHz. It was widely used in IBM PC compatible computers during the mid 1980s to early 1990s
|
|
| February 1, 1982 | ||
 |
|
|
|
January 1982 |
||
 |
|
|
| 1981 | ||
 |
the Chaos Computer Club was founded in Berlin by Wau Holland and others
|
|
| September 12, 1981 | ||
 |
the first cell phone network with automatic roaming was started in Saudi Arabia
|
|
| September 1981 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1981 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| ○
|
|
|
| 1981 | ||
| ○
|
Industry Standard Architecture
|
|
| 1981 | ||
| ○
|
the CGA graphics card gave 640x200 resolution with 16 colors
|
|
| 1981 | ||
 |
with the release of the IBM PC began the WinTel (Windows-Intel) monopoly
|
|
| August 12, 1981 | ||
| ○
|
IBM announced the System/23 Datamaster
|
|
| July 28, 1981 | ||
 |
Microsoft bought all rights to 86-DOS from Seattle Computer Products for US$50,000, and the name MS-DOS was adopted
|
|
| July 27, 1981 | ||
 |
the Xerox Star was the first computer to feature a WIMP (window, icon, menu, pointing device) graphical user interface
|
|
| 1981 | ||
 |
the Osborne 1 was one of the first portable computers. Despite its interesting characteristics, Osborne Computer Corporation suffered the competition of the first IBM PC compatibles and went bankrupt in 1983
|
|
| April 1981 | ||
 |
MIDI is an industry-standard protocol that defines each note precisely and concisely, allowing electronic musical instruments and computers to exchange data
|
|
| 1981 | ||
| ○
|
Seagate Technology created the first hard disk drive for microcomputers the disk held 5 megabytes of data, five times as much as a standard floppy disk, and fit in the space of a floppy disk drive
|
|
| 1980 | ||
|
|
|
| 1980 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1980 | ||
 |
the optical mouse was invented by Steven T. Kirsch
|
|
| 1980 | ||
| ○
|
Tim Berners-Lee wrote a hyperlinking program called Enquire which eventually evolved into the World Wide Web
|
|
| 1980 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1980 | ||
 |
|
|
| March 1980 | ||
| ○
|
the first router was created at Stanford University by a staff researcher named William Yeager
|
|
| January 1980 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1979-2003 | ||
| ○
|
the Perq graphical workstation
|
|
| 1979 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1979 | ||
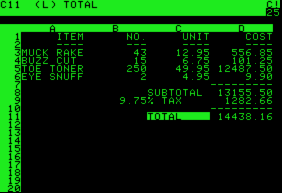 |
VisiCalc was the first spreadsheet program available for personal computers. It was the application that turned the microcomputer from a hobby for computer enthusiasts into a business tool. After the Apple II version, VisiCalc was also released for the Atari 8-bit family, the Commodore PET (both based on the MOS Technology 6502 processor, like the Apple), and the IBM PC
|
|
| 1979 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1979 | ||
 |
UUCP stands for Unix to Unix Copy Protocol, and is a computer program and protocol allowing remote execution of commands and transfer of files, email and netnews between Unix computers not connected to the Internet proper. In 1979 Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis of Duke University created Usenet a distributed Internet discussion system that evolved from a general purpose UUCP network. Now widely recognized concepts and terms such as "FAQ" and "spam" were originated on the usenet
|
|
| 1978 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1978 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1978 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1978-2007 | ||
 |
the Speak & Spell talking learning aid
|
|
| 1978 | ||
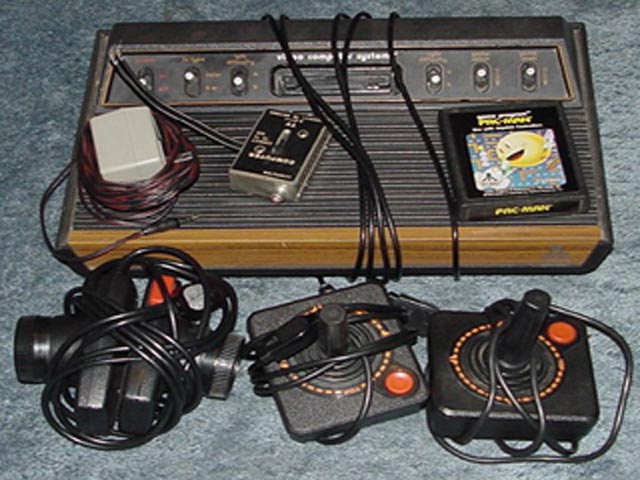 |
the Atari VCS was the first successful video game console to use plug-in cartridges instead of having one or more games built in. It was later renamed as the Atari 2600
|
|
| October 1977 | ||
 |
|
|
| August 3, 1977 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1977 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1977 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
the Apple II was the first PC with color graphics. Customers used their own TV sets as monitors and audiocassette recorders for data storage
|
|
| June 5, 1977 | ||
 |
the Apple I was the first computer to combine a keyboard with a microprocessor and a connection to a monitor. Designed by Steve Wozniak and Steve Jobs, it was sold as Apple's first product
|
|
| April 1976 | ||
|
PostScript
|
|
|
| 1976 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1976 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1976 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| February 3, 1976 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1970s | ||
 |
|
|
| September 1975 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1975 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1975 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1975 | ||
 |
the IBM 5100 Portable Computer weighed about 25 kg
|
|
| September 1975 | ||
 |
the CCD flatbed scanner was invented by Ray Kurzweil
|
|
| 1975 | ||
 |
the Homebrew Computer Club had its first meeting
|
|
| March 1975 | ||
 |
Micro-Soft was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen. Their first product was Altair BASIC - the first programming language for the world's first truly personal computer, the MITS Altair 8800. Gates and Allen had already founded Traf-o-Data, their first company, in 1972
|
|
| 1975 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
the MITS Altair 8800 was a microcomputer design based on the Intel 8080A CPU. Sold as a kit through Popular Electronics magazine, the designers intended to sell only a few hundred to hobbyists, and were surprised when they sold over ten times that many in the first month
|
|
| 1975 | ||
 |
Marsh’s Supermarket in Troy, Ohio was the first to use the bar-code for scanning groceries
|
|
| June 1974 | ||

|
the Intel 8080 is an 8-bit CPU generally considered to be the first truly usable microprocessor CPU design. The 8080 was used in many early computers, such as the MITS Altair 8800 and IMSAI 8080, forming the basis for machines running the CP/M operating system
|
|
| April 1974 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 19?? | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 19?? | ||
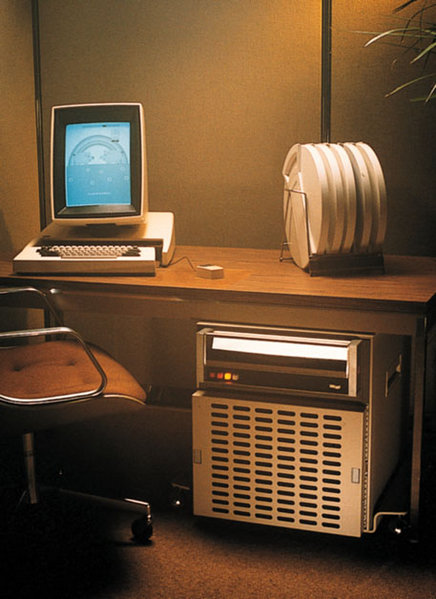 |
the Xerox Alto was the first personal computer and the first computer to use the desktop metaphor and graphical user interface (GUI)
|
|
| 1973 | ||
 |
the Micral industrial microcomputer was based on the Intel 8008
|
|
| 1973 | ||
| ○
|
Plankalkül was first published the first compiler for it was implemented in 2000 by the Free University of Berlin
|
|
| 1972 | ||
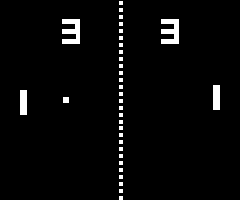 |
Pong an adaptation of table tennis to the video screen, was the first commercially successful video game. It was released by Atari
|
|
| 1972 | ||
 |
the Magnavox Odyssey was the first home video game console
|
|
| 1972 | ||
 |
the original laser printer called EARS was developed at the Xerox Palo Alto Research Center. The Xerox 9700 Electronic Printing System, the first xerographic laser printer product, was released in 1977
|
|
| 1971 | ||
 |
the floppy disk became a standard part of the IBM System/370
|
|
| 1971 | ||
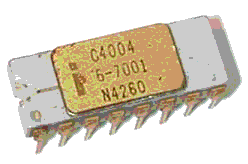 |
the Intel 4004 a 4-bit CPU, was the world's first single-chip microprocessor. The chief designers of the chip were Ted Hoff and Federico Faggin of Intel and Masatoshi Shima of Busicom.´The chip was originally designed for the Japanese company Busicom to be used in their line of calculators
|
|
| November 15, 1971 | ||
| ○
|
fourth generation computers are build with microprocessors. The earliest models were capable of 10,000,000 calculations per second
|
|
| 1971-present | ||
|
@
|
the use of the at sign was introduced by Ray Tomlinson. Email had started in 1965
|
|
| 1971 | ||
| ○
|
the electronic touch interface was invented by Dr. Samuel C. Hurst
|
|
| 1971 | ||
 |
the term Silicon Valley was coined by journalist Don C. Hoefler. Silicon refers to the high concentration of semiconductor and computer-related industries in the area; Valley refers to the Santa Clara Valley
|
|
| 1971 | ||
 |
Esquire magazine published Secrets of the Little Blue Box with instructions for making a blue box among the perpetrators: college kids Steve Wozniak and Steve Jobs, future founders of Apple Computer, who launch a home industry making and selling blue boxes
|
|
| 1971 | ||
 |
Bowmar Instruments Corp. introduces the Bowmar Brain, the first pocket calculator for the masses
|
|
| 1971 | ||

|
the Texas Instruments TMS 1000 was a 4 bit processor, designed for use in video games, microwave ovens, calculators and other electronics products. It was arguably the first microcontroller developed, and was introduced on the market in 1974
|
|
| 1971 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1971 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1970s | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1970 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1970 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1970 | ||
 |
Unix was officially named and ran on the PDP-11/20. The operating system was developed in the 1960s by a group of AT&T Bell Labs employees
|
|
| 1970 | ||
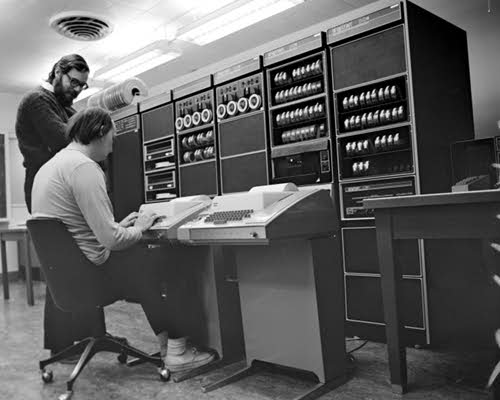 |
|
|
| 1970 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
|
|
| 1970 | ||
|
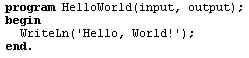
Pascal is based on the Algol programming language and is named in honor of mathematician and philosopher Blaise Pascal
|
|
| 1970 | ||
 |
the Honeywell H316 "Kitchen Computer"
|
|
| 1969 | ||
 |
C is a programming language named "C" because many of its features were derived from an earlier language called "B"
|
|
| 1969 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1969 | ||
| ○
|
Joe Engressia ('The Whistler', 'Joybubbles' and 'High Rise Joe') invented phreaking
|
|
| 1969 | ||
 |
the Arpanet of the U.S. Department of Defense was the world's first operational packet switching network, and the progenitor of the global Internet
|
|
| October 29, 1969 | ||
 |
Douglas C. Engelbart and the group of 17 researchers working with him in the Augmentation Research Center at Stanford Research Institute in Menlo Park, CA, presented a 90- minute live public demonstration of the online system, NLS, they had been working on since 1962
|
|
| December 9, 1968 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
| ○
|
||
| 1968 | ||
 |
|
|
| late 1960s | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1968 | ||
 |
the Art of Computer Programming by Donald Knuth
|
|
| 1968 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1968 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1967 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1966 | ||
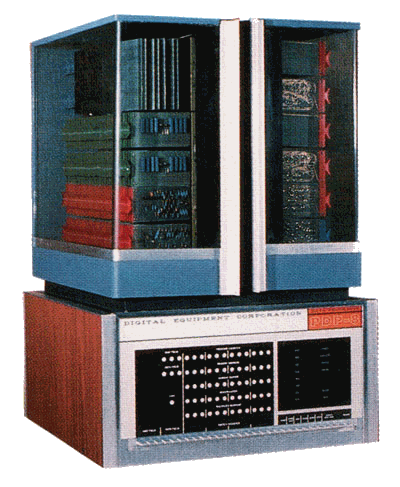 |
the PDP-8 was the first successful commercial minicomputer
|
|
| March 22, 1965 | ||
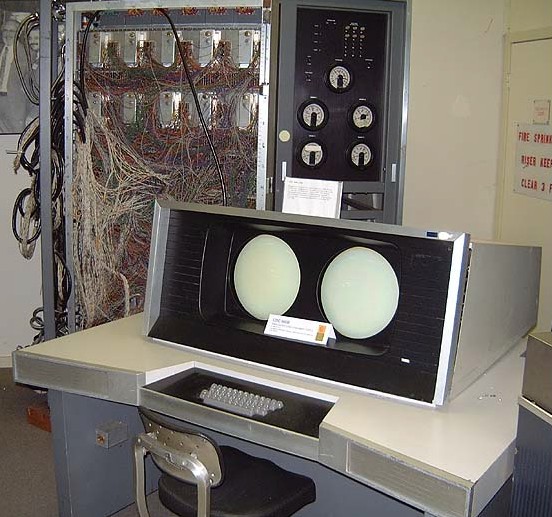 |
the CDC 6600 is generally considered to be the first successful supercomputer,outperforming the fastest machines of the era by about three times. It remained the world's fastest computer from 1964 to 1969, when it relenquished that status to its successor, the CDC 7600
|
|
| 1965 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1964 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1964 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
|
|
| April 7, 1964 | ||
| ○
|
third generation computers used integrated circuits for the first time. They achieved 1,000,000 calculations per second |
|
| 1964-1971 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1964 | ||
 |
the BASIC programming language was devised by Profs. John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz of Dartmouth College
|
|
| 1963 | ||

|
the IEEE is an international non-profit, professional organization for the advancement of technology related to electricity
|
|
| 1963 | ||
| ○
|
Sketchpad was the first program ever to utilize a complete graphical user interface and is considered to be the ancestor of modern computer-aided drafting (CAD) programs
|
|
| 1963 | ||
 |
the first computer mouse was invented by Douglas Engelbart of the Stanford Research Institute
|
|
| 1963 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1963 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1963 | ||
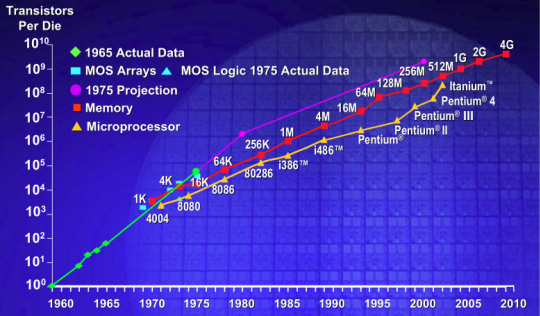 |
Intel's chairman Gordon Moore suggested that integrated circuits would double in complexity every year while prices will stay the same. This suggestion will be known as Moore's Law
|
|
| 1963 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1962 | ||
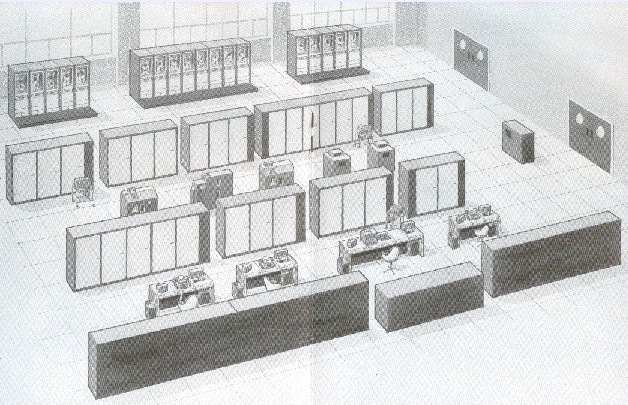 |
the ATLAS computer of the University of Manchester was arguably the fastest computer in the world until the release of the CDC 6600
|
|
| 1962 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1962 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1960s | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1961 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1961 | ||
| ○
|
the metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor was invented by Dawon Kahng and Martin Atalla at Bell Labs |
|
| 1960 | ||
| ○
|
Project Xanadu was founded by Ted Nelson as the original hypertext project
|
|
| 1960 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1960 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1960 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1960 | ||
 |
the PDP-1 was the first computer in Digital Equipment's PDP series and is famous for being the computer most important in the creation of hacker culture, at MIT, BBN and elsewhere
|
|
| 1960 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
|
|
| 1959 | ||
| ○
|
Jean Hoerni's Planar process
|
|
| 1959 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1959 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1959 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1958 | ||
|
|
|
| 1958 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1957 | ||
 |
the LA30 was a 30 character/second dot matrix printer produced by Digital Equipment Corporation of Maynard, Massachusetts
|
|
| 1957 | ||
 |
the drum scanner was developed for the SEAC computer
|
|
| 1957 | ||
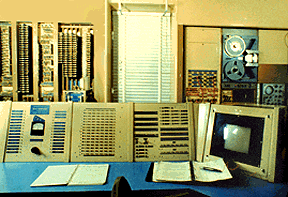 |
the first transistorized computer the TX-O was completed at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
|
|
| 1956 | ||
| ○
|
second generation computers were built with transistors and achieved 10,000 calculations per second |
|
| 1956-1963 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1956 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1955 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1955 | ||
 |
Texas Instruments was the first company to start commercial production of silicon transistors
|
|
| 1954 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| October 1954-2003 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1954 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
the first Fortran compiler was developed for the IBM 704 by a team led by John W. Backus. The language was widely adopted by scientists for writing numerically intensive programs, which encouraged compiler writers to produce compilers that generate faster code
|
|
| 1954 | ||
 |
the IBM 650 was the world’s first mass-produced computer. Over 2000 systems were produced between its introduction in 1954 and its final manufacture in 1962
|
|
| 1954 | ||
 |
the first high-speed printer was developed by Remington-Rand for use on the Univac computer
|
|
| 1953 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
the IBM 701 known as the Defense Calculator while in development, was IBM’s first commercial scientific computer. Its business computer sibling was the IBM 650
|
|
| April 7, 1953 | ||
 |
the hard disk was developed Reynold Johnson. The first computer with a hard disk drive as standard was the IBM 350 Disk File, introduced in 1956 with the IBM 305 computer
|
|
| 1952 | ||
 |
John von Neumann´s IAS computer became operational at the Institute for Advanced Studies in Princeton, N.J.
|
|
| 1952 | ||
.jpg) |
the LEO I was the first computer used for commercial business applications
|
|
| November 1951 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1951 | ||
 |
the UNIVAC I was the first commercial computer made in the United States. A-0 was the name of the programming language used on this computer and its successor the UNIVAC II
|
|
| March 31, 1951 | ||
 |
|
|
| February 1951 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1951 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1950 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
the Whirlwind computer developed at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology was the first computer that operated in real time, used video displays for output, and the first that was not simply an electronic replacement of older mechanical systems
|
|
| 1950 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1950 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
the Z4 was the first commercially available computer
|
|
| September 1950 | ||
 |
|
|
| May 6, 1949 | ||
 |
the Manchester Mark I is historically significant due to its pioneering inclusion of a kind of index registers in its architecture, as well as being the platform on which Autocode was developed, one of the first "high-level" computer languages
|
|
| early April 1949 | ||
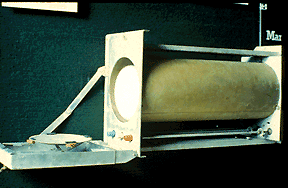 |
the Williams Tube was the first Random Access Memory and provided the medium on which the first ever electronically stored-memory program was written in the Manchester Mark I computer
|
|
| 1948 | ||
 |
the SSEM aka Baby was the first stored-program computer to run a program and to implement the main features of the von Neumann Architecture. The SSEM developed into the Manchester Mark I, which led to the Ferranti Mark I
|
|
| June 21, 1948 | ||
 |
Shockley's Junction-Transistor
|
|
| January 1948 | ||
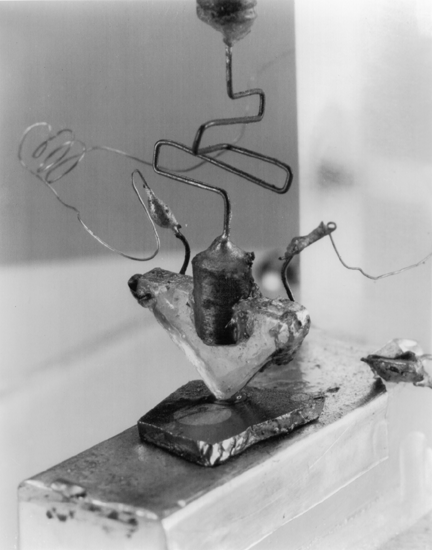 |
the Transistor was invented at Bell Telephone Laboratories by John Bardeen, Walter Houser Brattain, and William Bradford Shockley. Ironically, they had set out to manufacture a field-effect transistor (FET) predicted by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld as early as 1925 but eventually discovered current amplification in the point-contact transistor that subsequently evolved to become the bipolar junction transistor (BJT). The transistor, considered by many to be one of the greatest inventions in modern history, ranks with the printing press and the telephone. It is the key active component in practically all modern electronics
|
|
| December 23, 1947 | ||
| ○
|
the ACE was designed by Alan Turing
|
|
| February 19, 1946 | ||
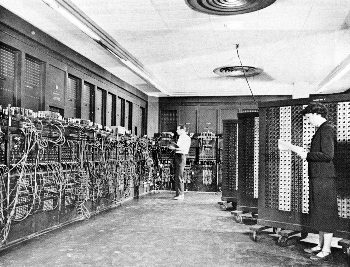 |
the ENIAC short for Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer, was the first all-electronic computer designed to be Turing-complete
|
|
| February 14, 1946 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1945 | ||
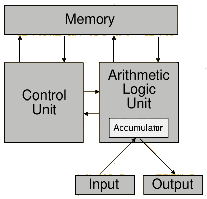 |
|
|
|
|
||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
| ○
|
the First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC by John von Neumann
|
|
| June 30, 1945 | ||
| ○
|
Thomas J. Watson Research Center
|
|
| 1945 | ||
 |
|
|
| June 1944 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
 |
the Harvard Mark I was also called the IBM ASCC, the Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator
|
|
| December 1943 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1943 | ||
|
|
the Church-Turing thesis was first proposed by Stephen C. Kleene but named after Alonzo Church and Alan Turing |
|
| 1943 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
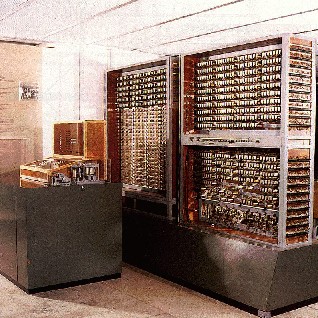 |
the Z3 was developed by Konrad Zuse and was the earliest working computer that has been shown to be Turing-complete
|
|
| 1941 | ||
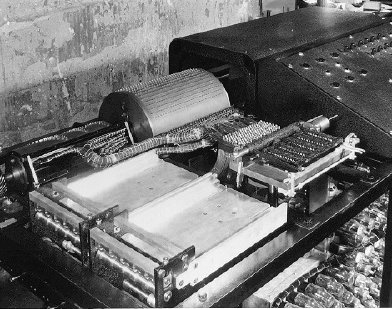 |
the Atanasoff-Berry Computer has been described as the first "electronic digital computer". However, it was not a stored program machine, which distinguishes it from later machines
|
|
| November 1939 | ||
 |
the Lorenz SZ 40 was a cipher machine used during World War II
|
|
| 1939 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1939 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1938 | ||
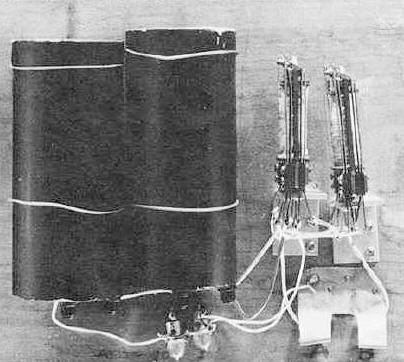 |
George Stibitz, then working at Bell Labs completed a relay-based computer he dubbed the Model K which calculated using binary addition
|
|
| November 1937 | ||
| ○
|
first generation computers used vacuum tubes and achieved 1,000 calculations per second
|
|
| 1937-1956 | ||
| ○
|
Claude Shannon's A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits
|
|
| 1937 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
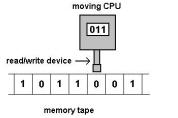 |
Turing machines were described by Alan Turing
|
|
| 1936 | ||
|
λ x. x + 1
|
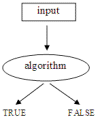
Alonzo Church used lambda calculus to give a negative answer to the Entscheidungsproblem |
|
| 1936 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1936 | ||
| ○
|
IBM provided the Third Reich with punch card machines that helped the Nazis increase the efficiency of the Holocaust |
|
| 1930s-1940s | ||
| ○
|
Gödel's incompleteness theorems
|
|
| 1931 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1929 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1928 | ||
| ○
|
the Ackermann function is a not primitive recursive function
|
|
| 1928 | ||
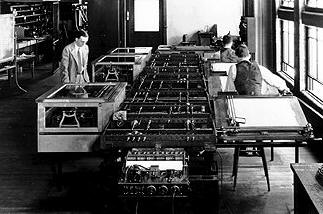 |
a practical version of the differential analyser which was invented in 1876 by James Thomson, was first constructed by H. W. Nieman and Vannevar Bush at MIT
|
|
| 1927 | ||
 |
the Model 12 was the first general purpose teletype
|
|
| 1922 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1919 | ||
 |
the Enigma machine was a portable cipher machine used to encrypt and decrypt secret messages
|
|
| 1917 | ||
 |
the Monroe High-Speed Adding Calculator
|
|
| 1914 | ||

|
IBM was born when Herman Hollerith's Tabulating Machine Co. merged with two other companies to form the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (C-T-R for short). In 1924 it changed its name to International Business Machines
|
|
| 1911 | ||
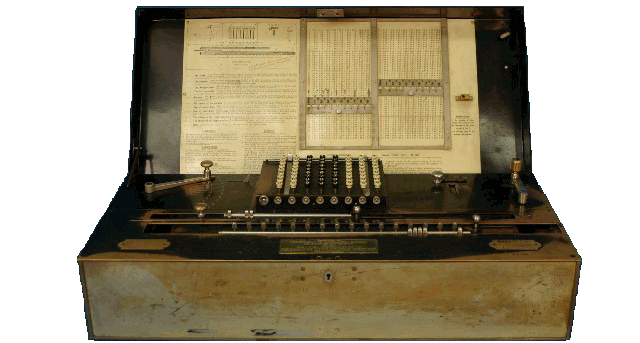 |
the Millionaire Calculator was developed by Otto Steiger and built in Zurich by the firm of Hans W. Egli
|
|
| 1892 | ||
 |
the eleventh United States Census was the first to be compiled on a tabulating machine, developed by Herman Hollerith
|
|
| 1890 | ||
| ○
|
Dedekind introduced primitive recursive functions |
|
| 1888 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1888 | ||
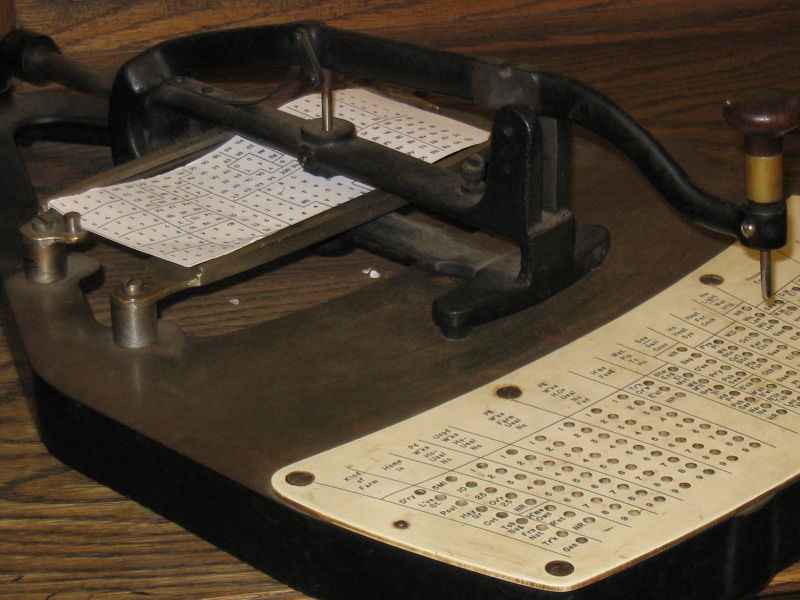 |
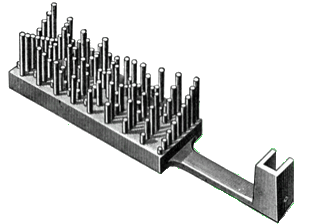
the modern punch card was a patent by Herman Hollerith, it was used as an input method for calculating machines, as well as music machines
|
|
| June 8, 1887 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1887 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1886 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
|
|
| 1869 | ||
 |
the QWERTY keyboard was invented by Christopher Sholes
|
|
| 1863 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
| 1854 | ||
 |
Ada Byron's notes on the Analytical engine
|
|
| 1842 | ||
| ○
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
|
|
| 1837 | ||
| ○
|
the relay was invented by Joseph Henry
|
|
| 1837 | ||
 |
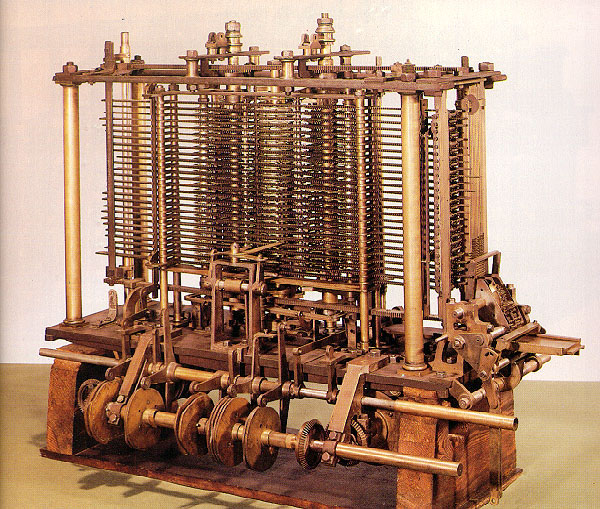
a model for a Difference engine was presented to the Royal Astronomical Society in a paper entitled "Note on the application of machinery to the computation of astronomical and mathematical tables" by Charles Babbage (1791-1871). Between 1833 and 1842 he tried to build a machine that would be programmable to do any kind of calculation, not just ones relating to polynomial equations. The first breakthrough came when he redirected the machine's output to the input for further equations. He described this as the machine "eating its own tail". It did not take much longer for him to define the main points of his analytical engine
|
|
| June 14, 1822 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1820 | ||
 |
the Jacquard loom used the holes punched in pasteboard punch cards to control the weaving of patterns in fabric
|
|
| 1801 | ||
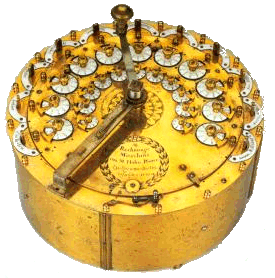 |
Mathieus Hahn designed the first functional mechanical calculator
|
|
| 1773 | ||
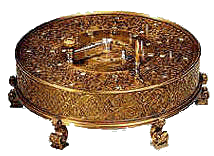 |
Antonius Braun developed the first calculator with the four base calculations
|
|
| 1727 | ||
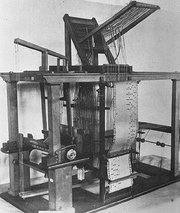 |
a loom controled by perforated paper tape was invented by Basile Bouchon. In 1726 his co-worker Jean-Baptiste Falcon improved on his design by using perforated paper cards attached to one another, which made it easier to quickly change the program Further refinements by others eventually lead to the wildly successful Jacquard loom
|
|
| 1725 | ||
| ○
|
Giovanni Poleni's Pinwheel calculator
|
|
| 1709 | ||
 |
the binary system was invented by Leibniz, who published his ideas in the "Explication de l'Arithmétique Binaire" in 1703
|
|
| 1679 | ||
 |
the the step reckoner a mechanical calculator that could execute all four arithmetical operations was invented by Leibniz
|
|
| 1671 | ||
| ○
|
Leibniz' calculus ratiocinator
|
|
| 1667 | ||
 |
the Pascaline was the second mechanical calculator in history, invented by Blaise Pascal
|
|
| 1645 | ||
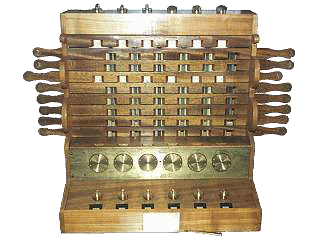 |
the first calculator was built by Wilhelm Schickard
|
|
| 1623 | ||
|
|
the slide rule was invented by William Oughtred
|
|
| 1622 | ||
 |
|
|
| 1617 | ||
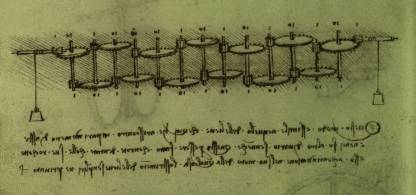 |
Leonardo da Vinci's ratio machine
|
|
| 1493 | ||
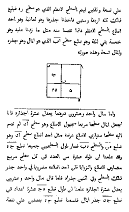 |
Al-Khawarizmi described an algorithm for solving Linear equations and Quadratic equations. The word algorithm comes from his name and was coined in the 18th century
|
|
| early 9th century | ||
 |
|
|
| 80 bc | ||
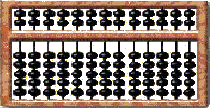 |
|
|
| 3000 bc | ||
| ○
|
counting rods were used by ancient Chinese before the invention of the abacus
|
|
| 4000 bc | ||
 |
the Ishango Bone is a tally stick, made of bone, which contains sequences of prime numbers, and some series of multiples. The bone was found in the area of the headwaters of the Nile River
|
|
| 20,000 bc |